იან . 10, 2025 09:41
Back to list
Welding Rods 6010 for welding carbon steel tubes
Metal welding rods are critical components in the welding industry, offering strength and versatility in various applications. Navigating the realm of metal welding rods can be complex due to the numerous options available. This discussion will delve into their characteristics, application processes, and selection criteria, focusing on delivering an experience-rich, expert-backed narrative that underscores authority and trustworthiness.
Beyond material selection, the operator’s skill level and the intended use environment profoundly influence the performance of welding rods. Professional welders with experience in different positions and environments can exploit the benefits of specific rod types to achieve seamless, robust joints. Moreover, expertise in tackling issues such as rod sticking, excessive spatter, or porosity defines the difference between novice and master welders. The authoritative use of welding rods is further enhanced by understanding their maintenance and handling protocols. Proper storage—away from moisture and contaminants—safeguards the rods from damage, which could otherwise lead to weld defects. Keeping open packages sealed and maintaining an inventory rotation can preserve rod integrity, ensuring consistent results. Trust in the application of welding rods is also a factor of adherence to safety standards and protocols. Welding is an inherently hazardous process that necessitates proper protective gear, such as helmets and gloves, shielding operators from the risks of molten metal and intense ultraviolet light. Compliance with industry safety regulations not only protects welders but also instills confidence in the quality of workmanship. In conclusion, choosing and using metal welding rods requires a balanced blend of experiential knowledge, technical expertise, and strict adherence to guidelines. Each aspect, from classification to storage, plays an integral role in achieving and sustaining high-quality welds. Thus, investing in understanding the nuances of welding rods and refining skills consistently can propel both novices and seasoned practitioners toward exceptional proficiency and craftsmanship in the art of welding.
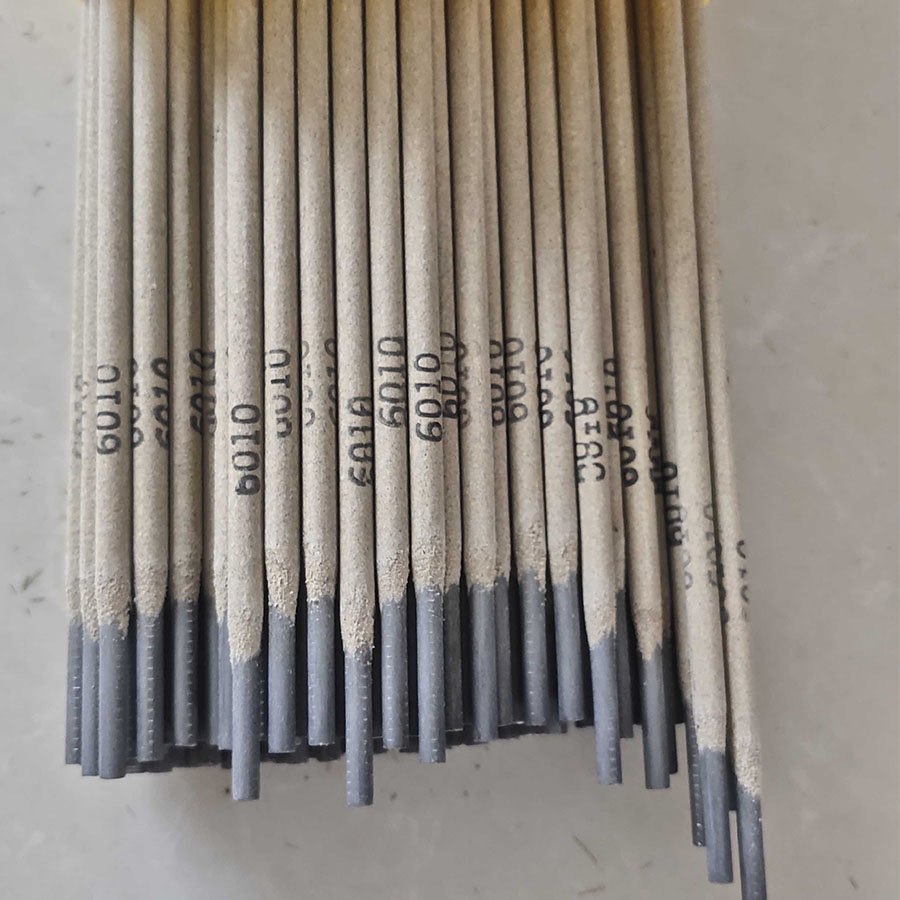

Beyond material selection, the operator’s skill level and the intended use environment profoundly influence the performance of welding rods. Professional welders with experience in different positions and environments can exploit the benefits of specific rod types to achieve seamless, robust joints. Moreover, expertise in tackling issues such as rod sticking, excessive spatter, or porosity defines the difference between novice and master welders. The authoritative use of welding rods is further enhanced by understanding their maintenance and handling protocols. Proper storage—away from moisture and contaminants—safeguards the rods from damage, which could otherwise lead to weld defects. Keeping open packages sealed and maintaining an inventory rotation can preserve rod integrity, ensuring consistent results. Trust in the application of welding rods is also a factor of adherence to safety standards and protocols. Welding is an inherently hazardous process that necessitates proper protective gear, such as helmets and gloves, shielding operators from the risks of molten metal and intense ultraviolet light. Compliance with industry safety regulations not only protects welders but also instills confidence in the quality of workmanship. In conclusion, choosing and using metal welding rods requires a balanced blend of experiential knowledge, technical expertise, and strict adherence to guidelines. Each aspect, from classification to storage, plays an integral role in achieving and sustaining high-quality welds. Thus, investing in understanding the nuances of welding rods and refining skills consistently can propel both novices and seasoned practitioners toward exceptional proficiency and craftsmanship in the art of welding.
Latest news
-
Premium AC Stainless Steel Welding Rods - Durable & Corrosion-ResistantNewsAug.05,2025
-
E7018 Welding Rods: Premium Low Hydrogen ElectrodesNewsAug.04,2025
-
High-Strength Cast Iron Welding Electrode AWS ENi-ClNewsAug.03,2025
-
E6011 Welding Rod | All-Position AC/DC ElectrodesNewsAug.02,2025
-
J422 Welding Rod: Durable Electrodes for Strong WeldsNewsAug.01,2025
-
AWS E7024 Arc Welding Electrodes: High-Efficiency & Easy UseNewsJul.31,2025


