-
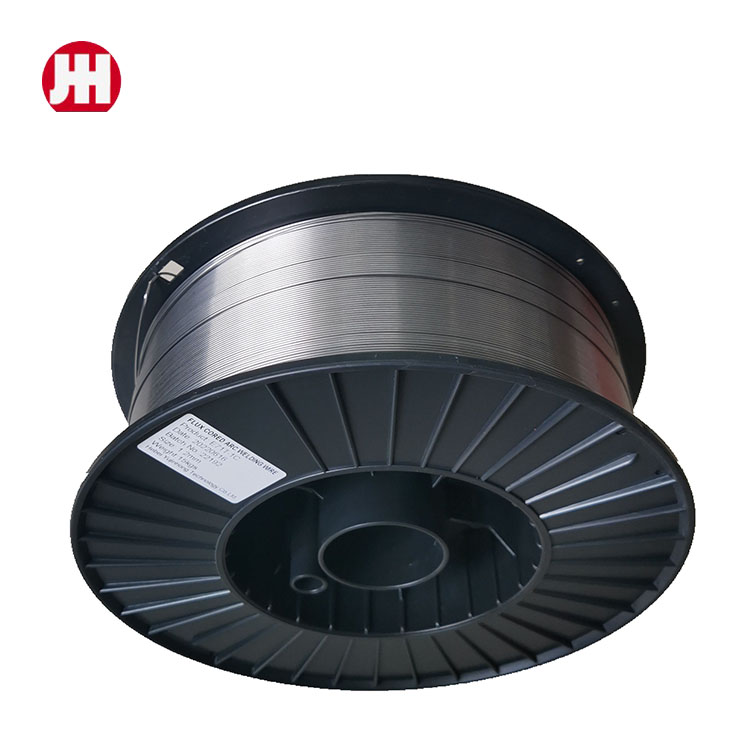 Wholesale MIG Aluminum Welding Wire Manufacturers A Comprehensive Guide In the manufMagbasa pa
Wholesale MIG Aluminum Welding Wire Manufacturers A Comprehensive Guide In the manufMagbasa pa -
 Leading Manufacturers of Wholesale Flux Cored Welding Wires for Industrial Applications and ProjectsWholesale Flux-Cored Welding Wire Manufacturers A Comprehensive Overview In the worlMagbasa pa
Leading Manufacturers of Wholesale Flux Cored Welding Wires for Industrial Applications and ProjectsWholesale Flux-Cored Welding Wire Manufacturers A Comprehensive Overview In the worlMagbasa pa -
 The Rise of China’s Flux-Cored Aluminum Wire Factories China has established itself aMagbasa pa
The Rise of China’s Flux-Cored Aluminum Wire Factories China has established itself aMagbasa pa -
 The Rise of Copper Coated Welded Wire A New Era in Wire Solutions In an era where inMagbasa pa
The Rise of Copper Coated Welded Wire A New Era in Wire Solutions In an era where inMagbasa pa -
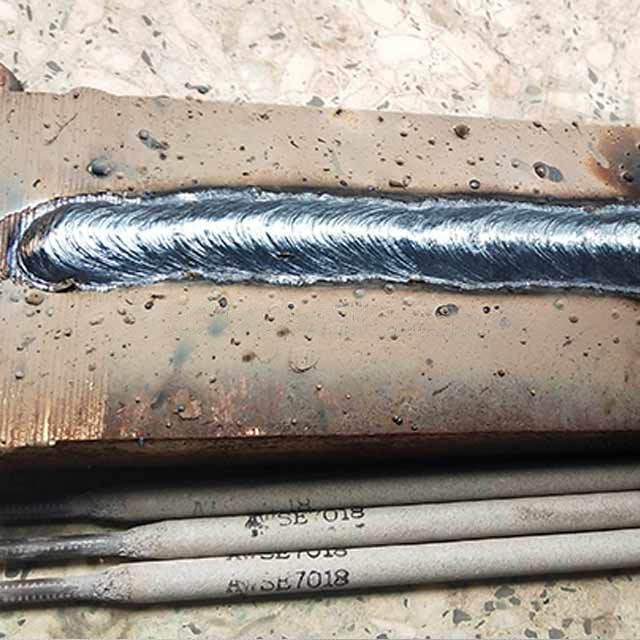 Tubular Welding Wire An Overview Tubular welding wire is a specialized type of weldiMagbasa pa
Tubular Welding Wire An Overview Tubular welding wire is a specialized type of weldiMagbasa pa -
 Wholesale Welding Wire A Comprehensive Look at 250kg Drums Welding is a cornerstone oMagbasa pa
Wholesale Welding Wire A Comprehensive Look at 250kg Drums Welding is a cornerstone oMagbasa pa -
 Understanding 308L 16% Welding Rod Factories A Comprehensive Overview Welding is an iMagbasa pa
Understanding 308L 16% Welding Rod Factories A Comprehensive Overview Welding is an iMagbasa pa -
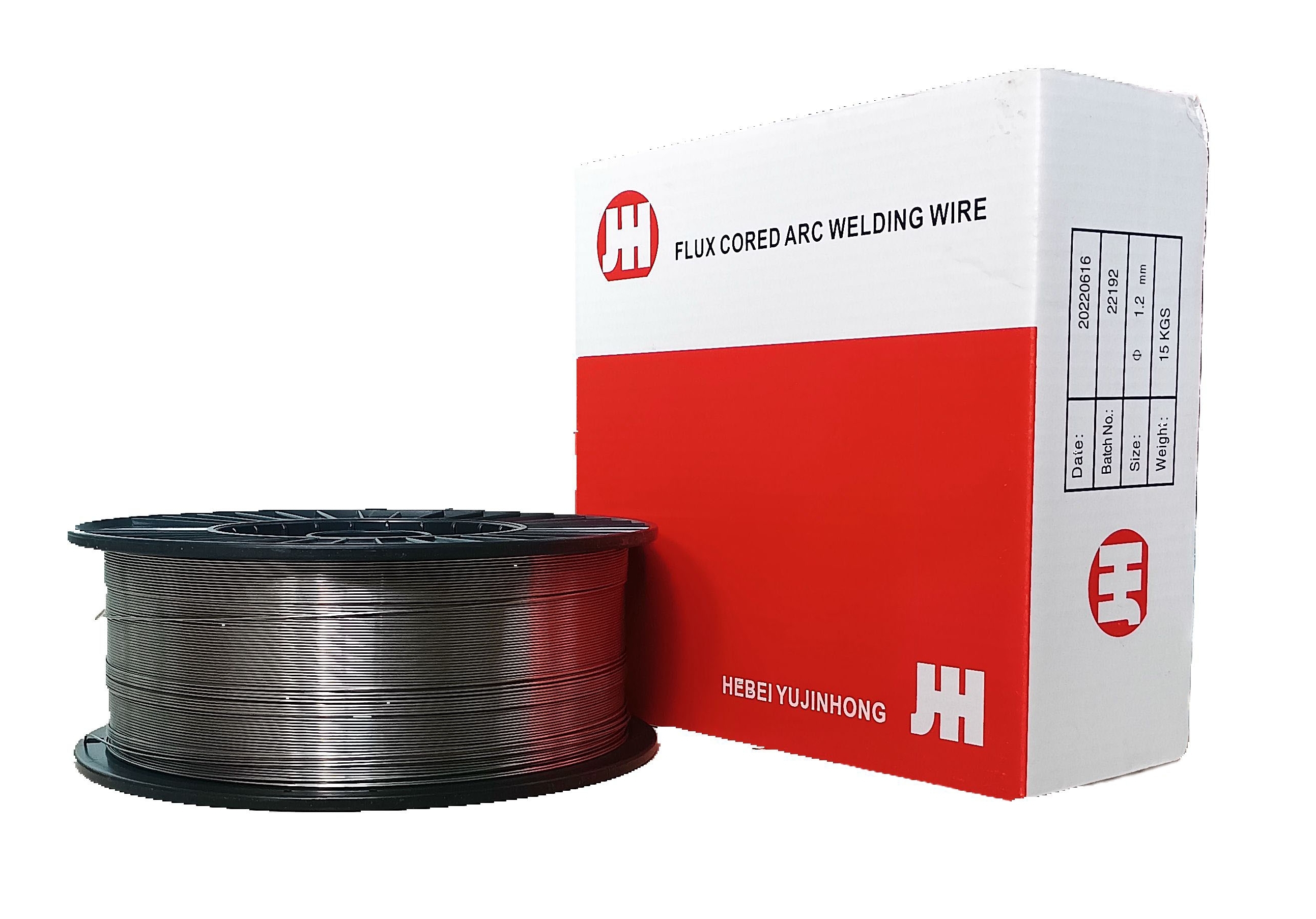 Exploring Wholesale Suppliers for E6011 Welding Electrode Welding is a critical induMagbasa pa
Exploring Wholesale Suppliers for E6011 Welding Electrode Welding is a critical induMagbasa pa -
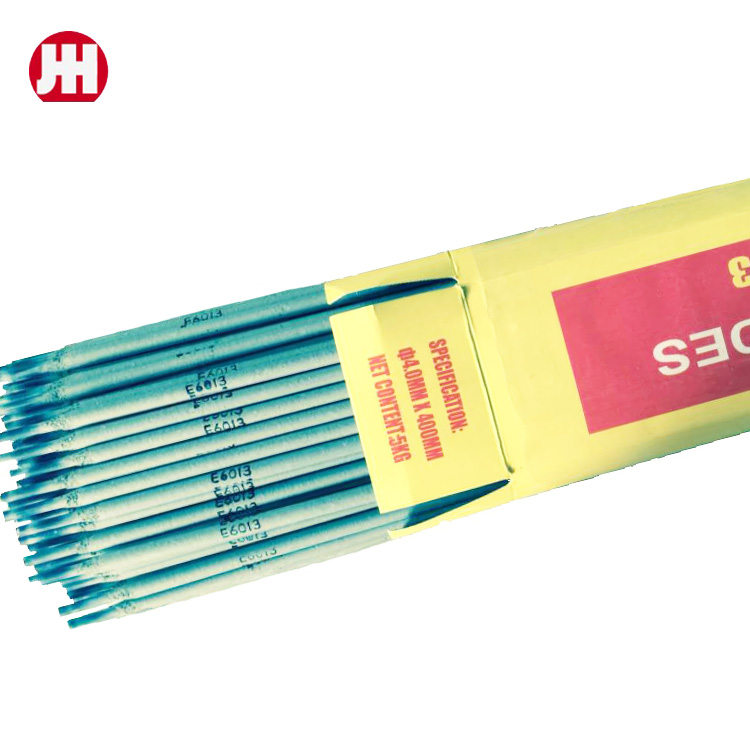 Exploring the Wholesale Electric Welding Rod Market A Focus on Factory Production InMagbasa pa
Exploring the Wholesale Electric Welding Rod Market A Focus on Factory Production InMagbasa pa -
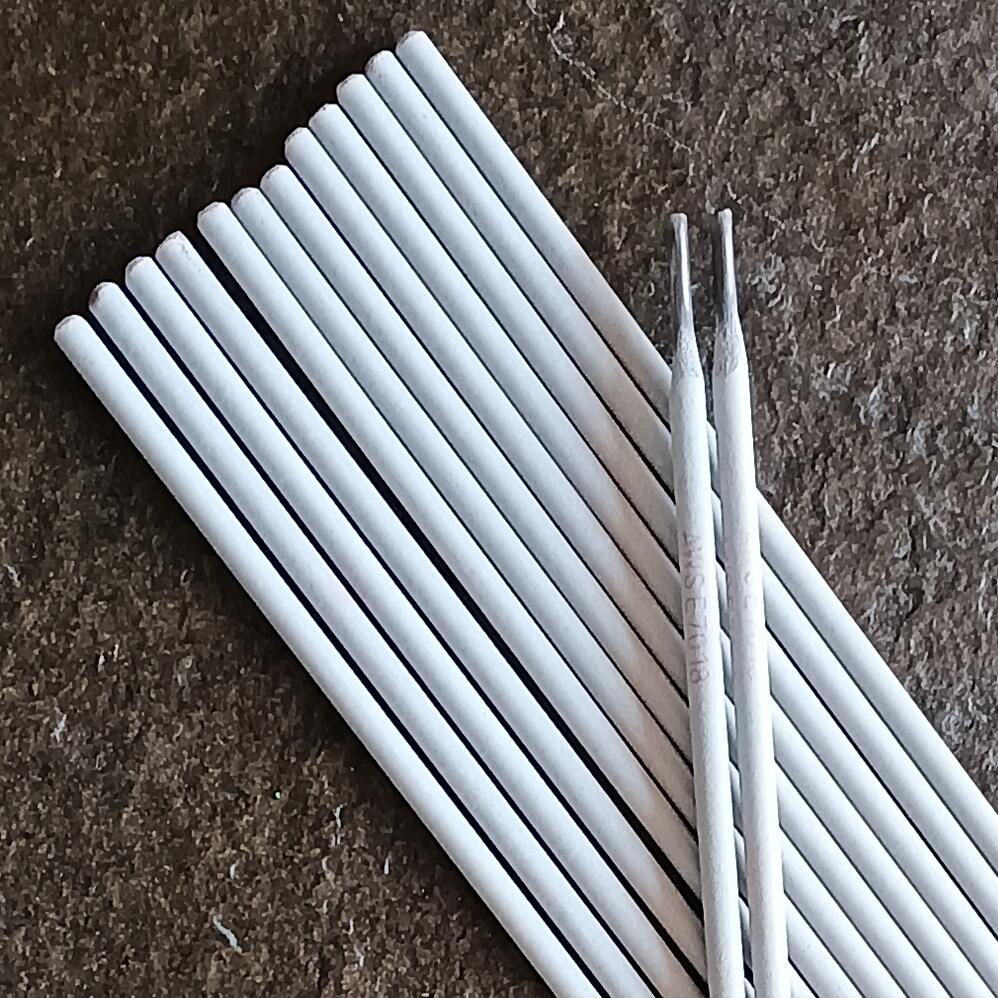 China 6011 1/8 Welding Rod Manufacturer An Overview of Quality and Innovations WeldinMagbasa pa
China 6011 1/8 Welding Rod Manufacturer An Overview of Quality and Innovations WeldinMagbasa pa -
 Understanding MIG Welding Wire The 1.2mm Standard MIG welding, or Metal Inert Gas weMagbasa pa
Understanding MIG Welding Wire The 1.2mm Standard MIG welding, or Metal Inert Gas weMagbasa pa -
 The Landscape of Electrode Wire Manufacturers in China China has established itselfMagbasa pa
The Landscape of Electrode Wire Manufacturers in China China has established itselfMagbasa pa


