焊条选择需要考虑几个因素
焊条选择需要考虑以下几个因素:
- 贱金属特性。您需要知道您将使用什么类型的金属、什么厚度的金属、基础金属的厚度、形状和接头装配。
- 抗拉强度。
Tensile strength refers to the maximum amount of stress that a material can experience while being either stretched or pulled before breaking or failing .
焊条的最小抗拉强度必须与母材的最小抗拉强度相匹配,以避免出现焊接不连续性,例如裂纹。
The welding electrodes used in most applications will be from either the 6000 or 7000 series. For example, an E6011 has a tensile strength of 60,000 psi. An E60 series welding rod will match the tensile strength of a mild steel according to Miller Welds.
- 焊接电流。
电极使用直流电和交流电是不同的。直流焊电弧稳定,但采用哪一种与焊条的性质有关。
例如采用J506碳钢碱性焊条。 J506虽然交直流均可使用,但直流焊接电弧稳定。使用交流电时,电弧不断断断,勉强进行焊接。
- 焊接位置。
选择使用哪种焊条时还必须考虑焊接位置。焊接位置是指钻工布置焊道的方向。
最常用的焊条是全位置焊条。主要焊接位置有4个。
Flat, Horizontal, Vertical, Overhead
大多数销售的焊条都是全位置焊条,但当您使用购买的设备时,查看焊条上的 4 或 5 位数字仍然是值得的。
- 规格和使用条件。
我应该使用什么尺寸的焊条?
通常,焊条的厚度应与您所使用的金属的厚度相匹配。
焊条可以安全处理的电流量取决于其直径。
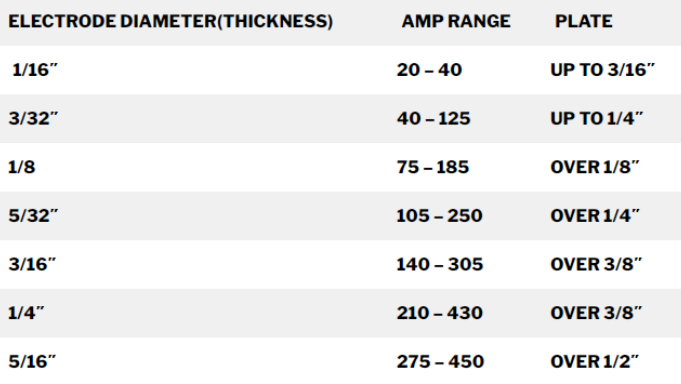
You can see the welding rod size charts that show the relationship between welding rod diameter and amperage, including this one produced by Firepower.
You can see in the chart that the welding rods range in size 5/64” in diameter to 5/32” in diameter.
该图表还显示了您将要焊接的母材的相应推荐板厚。
You will notice in this chart that there are welding rods ranging from 1/16” in diameter all the way up to 5/16” in diameter. Their chart looks something like this:
- T涂层材料
涂层材料
美国焊接协会 (AWS) 分类系统中包含 8 种不同类型的焊条涂层。
The coating material will determine which type of current, AC, DC+, or DC- that you will be using. As an example, high titania sodium and high titania potassium coatings are both compatible with AC current, but if you’re using DC- (direct current, negative polarity) then you will need to use a high titania sodium.
- 环境工作条件。
E6013电极:
拉伸强度为 60,000 psi:非常适合与低碳钢一起使用
是全位置电极:该电极可用于平放、水平、垂直和头顶位置
具有高钛钾涂层:兼容 AC 和 DC+ 电流
大多数入门级焊机都使用交流电流运行。找到与交流电流兼容的焊条并不困难,因为 8 种焊接涂层材料中有 6 种适用于交流电流。 E6013焊条易于使用的另一个原因是它产生的电弧较柔和,与E6011焊条相比,产生的熔渣更少。
The arc of the E6013 also doesn’t penetrate through the base metal quite as easily as the E6011 does, leaving some room for error for an operator who hasn’t yet gotten a feel for how closely the arc should be held from the base metal.


