Exploring the Production Process of High-Quality Welding Rods in a Modern Manufacturing Facility
The World of 3/4% Welding Rod Manufacturing
Welding is an essential process in various industries, and the quality of the welding materials used can significantly impact the strength and durability of welded joints. Among these materials, welding rods play a pivotal role. This article delves into the production and significance of 3/4% welding rods, focusing on their composition, manufacturing process, and applications.
Understanding Welding Rods
Welding rods, also known as electrodes, are comprised of metal or alloyed materials that are used to join two pieces of metal together through the process of welding. The rods help create a molten pool of metal that solidifies to form a strong bond once cooled. The designation 3/4% refers to the percentage of alloying elements present in the rod, which often includes elements like iron, manganese, silica, and nickel, depending upon the desired properties of the finished weld.
Composition and Properties
The composition of 3/4% welding rods is crucial as it affects the mechanical properties of the weld, including tensile strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. A 3/4% alloy typically provides a good balance of strength and flexibility, making it suitable for various applications. For instance, rods with this composition are commonly used in the construction of heavy machinery and structural components. The specific alloying elements contribute to the performance in terms of heat resistance and the ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing of 3/4% welding rods involves several stages, each critical to ensuring the quality of the final product. The first step is the selection of raw materials, which are sourced from reliable suppliers to guarantee consistency. Once the raw materials are gathered, they undergo a process of melting and alloying in specialized furnaces.
3/4 welding rod factory
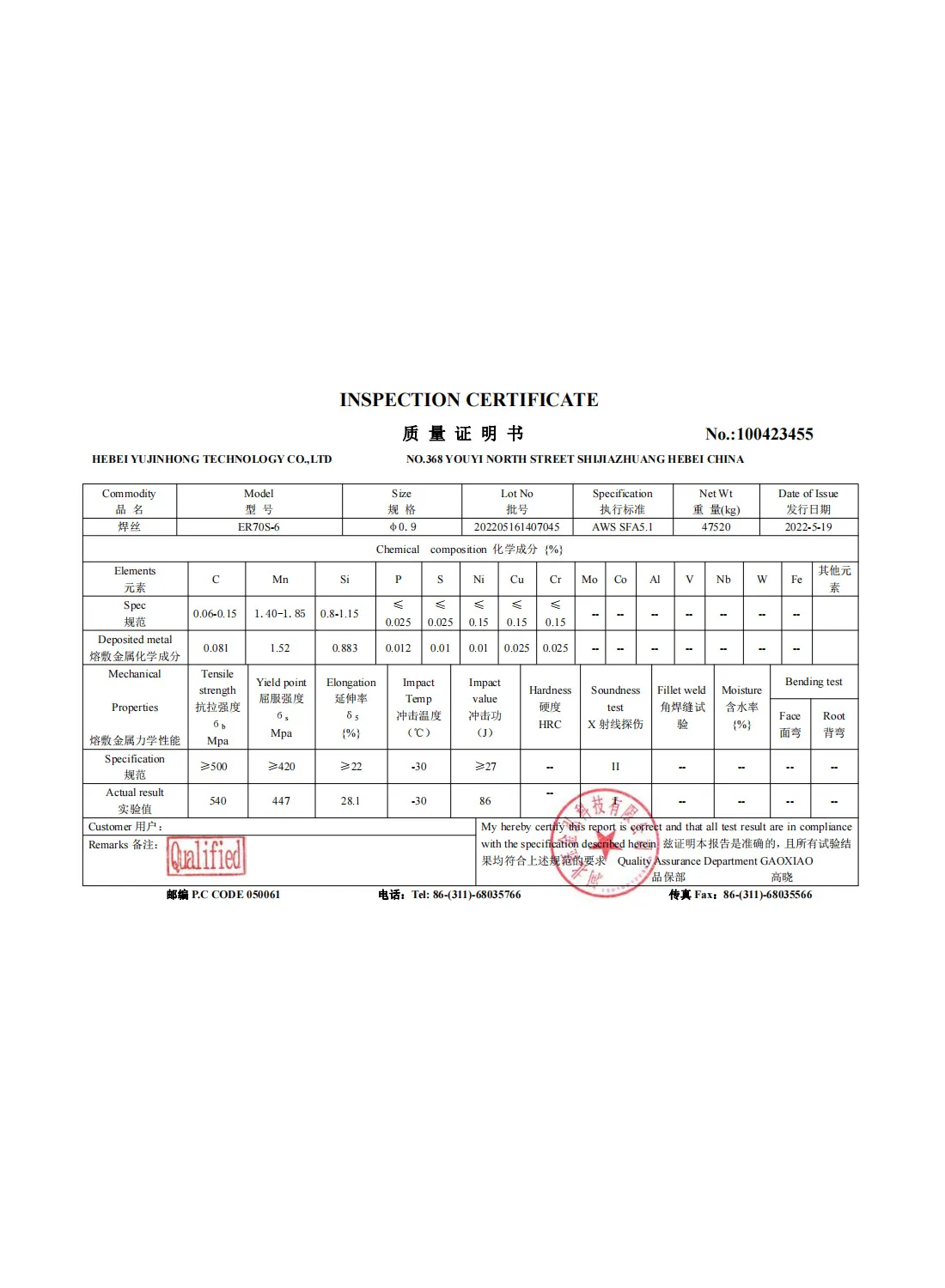
The molten metal is then cast into the desired shape, often in the form of billets or rods. After casting, these rods are subjected to a series of processes including forging, drawing, and heat treatment. Each of these steps is designed to enhance the mechanical properties of the welding rods. For instance, drawing the rods through a series of dies helps achieve the desired diameter and ensures uniformity across the batch.
Quality control is paramount throughout this process. Manufacturers conduct various tests to check for defects and ensure that the rods meet industry standards. This might include tensile testing, bend testing, and microscopic examinations to identify any inconsistencies in the microstructure.
Applications in Industry
3/4% welding rods are used in a diverse range of applications across several industries. In the construction sector, they are essential for building frameworks and reinforcing structural steel. Their robust properties make them ideal for applications that require high-strength welding, such as pipelines, pressure vessels, and shipbuilding.
In the automotive industry, these rods are employed in the manufacturing of vehicle frames and bodies. The ability to withstand stress and impact makes them suitable for a variety of automotive applications where safety and durability are paramount.
Moreover, the energy sector utilizes 3/4% welding rods for constructing power plants and pipelines. Their corrosion resistance ensures long-lasting performance in challenging environments.
Conclusion
The production of 3/4% welding rods is a complex yet fascinating process that plays a vital role in modern manufacturing and construction. With their balanced composition and exceptional properties, these welding rods contribute significantly to the strength and quality of welded joints in numerous applications. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for high-quality welding materials like 3/4% rods will undoubtedly grow, driving innovation and improvement in welding technology.
-
E316L Welding Rod: Premium 316L Stainless Steel WeldsNewsAug.11,2025
-
Premium SG2 Welding Wire | High-Quality MIG/MAG for SteelNewsAug.10,2025
-
E309 Welding Electrode: Premium Stainless Steel Stick RodsNewsAug.09,2025
-
Premium Solid MIG Wire for Strong, Reliable WeldsNewsAug.08,2025
-
E6010 Cellulose Electrode: Deep Penetration Steel Welding RodNewsAug.07,2025
-
Premium E316L Welding Rod for 316L Stainless SteelNewsAug.06,2025


